balance when replacement is necessary. Turbine blade maintenance and
replacement are covered in chapter 3.
1.24.
EXHAUST SECTION
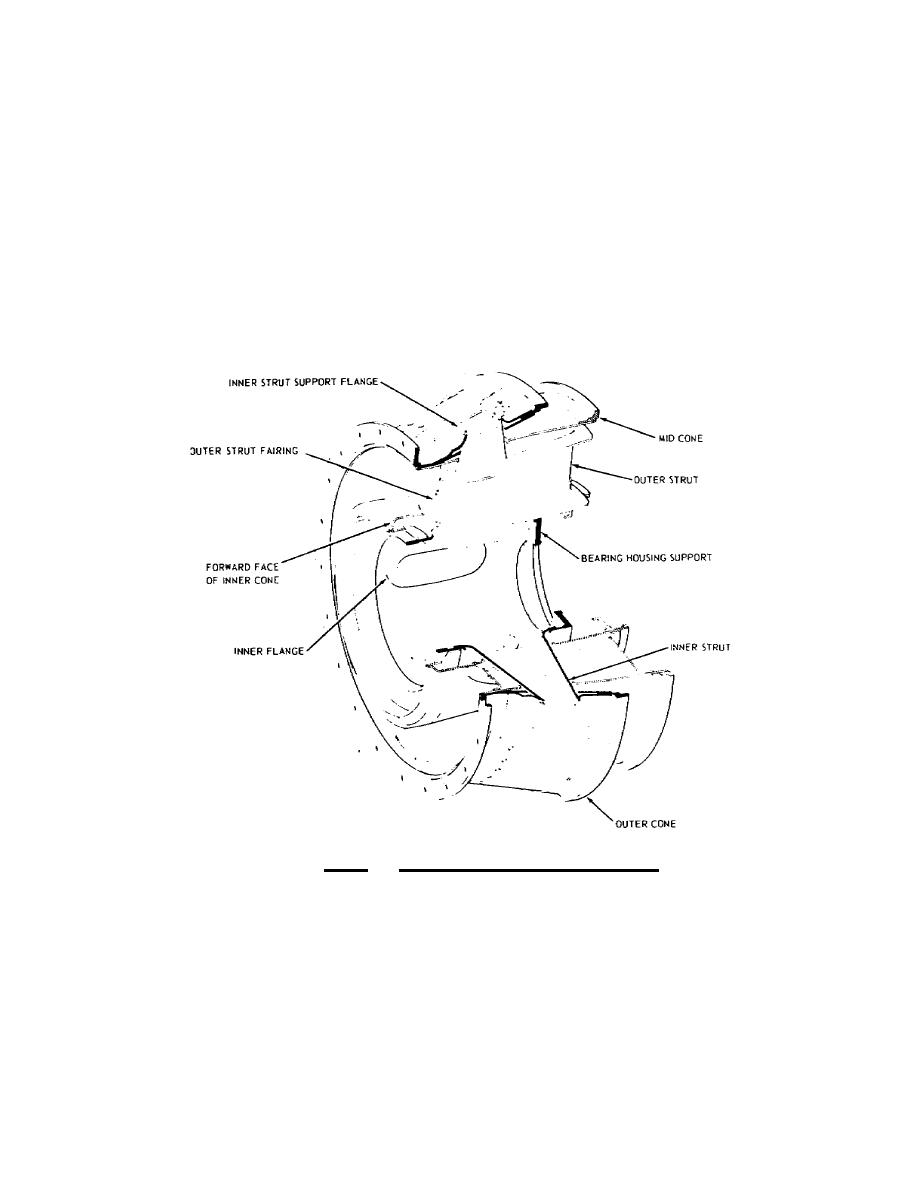
The hot gases are exhausted overboard through the exhaust
diffuser section. Internally, this section supports the power
turbine and aft portion of the powershaft. The exhaust diffuser is
composed of an inner and outer housing, separated by hollow struts
across the exhaust passage. The inner housing is capped by either a
tailcone or a cover plate which provides a chamber for cooling the
powershaft bearing. A typical exhaust diffuser section is shown in
figure 1.29.
Figure 1.29. Exhaust Diffuser Section.
Turboshaft engines used in helicopters do not develop thrust
by use of the exhaust duct. If thrust were developed by the engine
exhaust gas, it would be impossible to maintain a stationary hover;
therefore, helicopters use divergent ducts. These ducts reduce gas
velocity and dissipate any thrust remaining in the exhaust gases. On
fixed wing aircraft, the exhaust duct may be the convergent type,
which accelerates the remaining gases to produce thrust which adds
43



 Previous Page
Previous Page
