as the hovering air supply pattern is broken, dissymmetry of lift is created. As airspeed increases,
translational lift continues to improve up to the speed 'that is used for best climb.
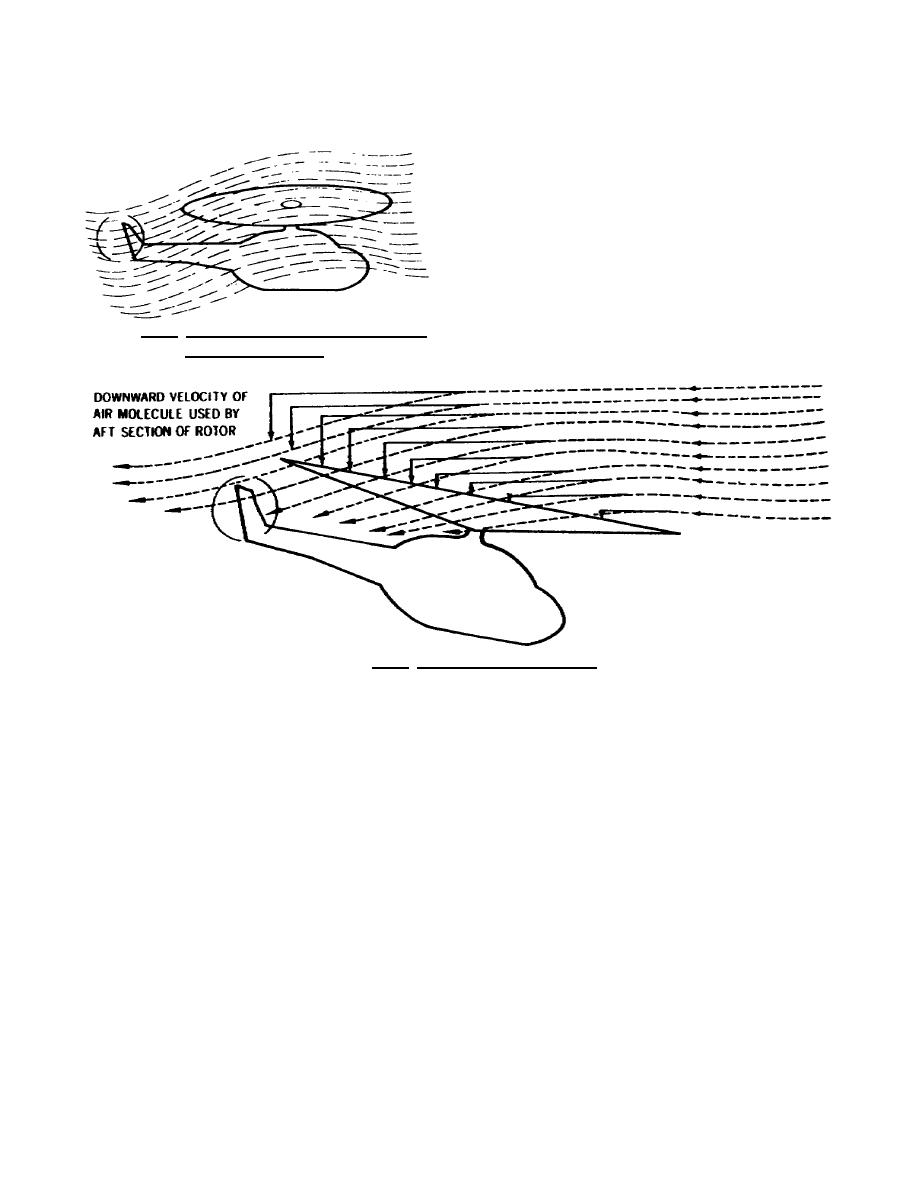
In forward flight, air passing through the
rear portion of the rotor disc has a higher
downwash velocity than the air passing through
the forward portion.
This is known as
transverse flow effect and is illustrated in figure
3.11.
This effect, in combination with
gyroscopic precession, causes the rotor to tilt
sideward and results in vibration that is most
noticeable on entry into effective translation.
Figure 3.10. Airflow with Translational Lift
in Forward Flight.
Figure 3.11. Transverse Flow Effect.
3.15.
AUTOROTATION
If engine power fails, or certain other emergencies occur, autorotation is a means of safely landing a
helicopter. The transmission in a helicopter is designed to allow the main rotor to turn freely in its
original direction when the engine stops. Figure 3.12 illustrates how the helicopter is allowed to glide to
earth and by using the main rotor rpm, make a soft landing.
The rotor blade autorotative driving region is the portion of the blade between 25 to 70 percent
radius, as shown in figure 3.13, blade element A. Because this region operates at a comparatively high
angle of
30



 Previous Page
Previous Page
